The Satpura Range: The Heart of Central India
India is home to several ancient mountain ranges that have shaped its geography, climate, and culture. Among them, the Satpura Range holds a special place as a vast and ecologically rich highland system stretching across central India. Though less famous than the Himalayas or the Western Ghats, the Satpuras play a crucial role in India’s natural and cultural landscape.
Origin and Meaning of the Name
The word “Satpura” comes from Sanskrit, meaning “seven folds” or “seven mountains.” This reflects the layered and rugged structure of the range, which consists of plateaus, hills, and deep valleys formed over millions of years through volcanic activity and erosion.
Geographic Extent
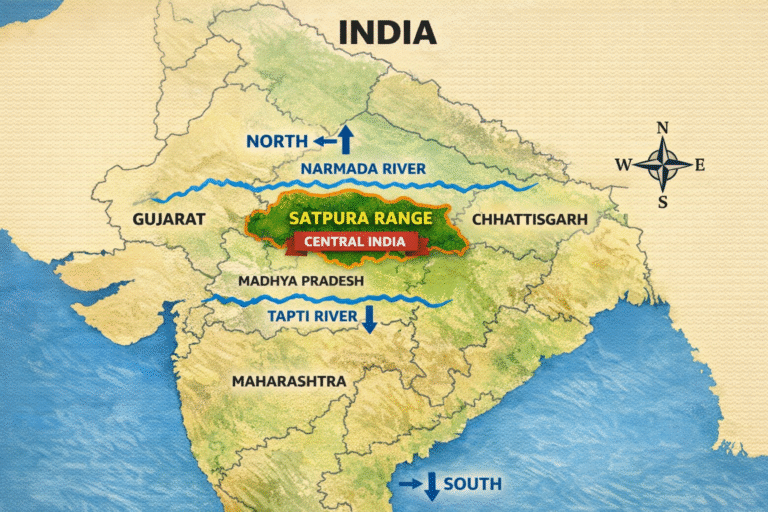
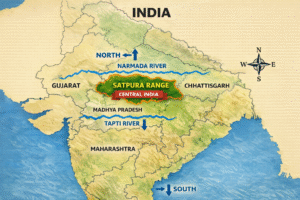
The Satpura Range runs east–west across central India, mainly through the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Chhattisgarh, with small extensions into Gujarat. It lies between two important river valleys:
-
The Narmada Valley to the north
-
The Tapti Valley to the south
This positioning makes the Satpuras a natural divide between northern and southern India.
Important Peaks and Plateaus
The highest peak of the Satpura Range is Dhupgarh (1,350 m), located near Pachmarhi in Madhya Pradesh. Other important regions include:
-
Mahadeo Hills

-
Maikal Range

-
Pachmarhi Plateau

These areas are known for their scenic beauty, cool climate, and dense forests.
Rivers and Drainage
The Satpura Range is a major watershed in central India. Several important rivers originate here, including:
-
Narmada
-
Tapti
-
Son
-
Wainganga
These rivers support agriculture, forests, and human settlements over large areas.
Climate and Biodiversity
The range supports tropical deciduous forests, rich in teak, sal, bamboo, and medicinal plants. It is also home to diverse wildlife such as:
-
Tigers
-
Leopards
-
Sloth bears
-
Gaur
-
Numerous bird species
Famous protected areas like Satpura National Park, Melghat Tiger Reserve, and Pench National Park are part of this ecosystem.
Geography and Location
The Satpura Range extends approximately 900 kilometers from eastern Gujarat through Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh into Chhattisgarh. It runs parallel to the Vindhya Range, bounded by the Narmada River to the north and Tapti River to the south, acting as a key watershed for rivers like the Godavari. Peaks rise up to 1,350 meters, with Dhupgarh as the highest, featuring tectonic formations from ancient uplift.greenverz+3
Biodiversity Hotspot
Satpura hosts diverse ecosystems, including teak-dominated forests, grasslands, and wildlife reserves like Satpura Tiger Reserve. It shelters tigers, leopards, sloth bears, and over 300 bird species, making it a conservation priority in central Indian highlands. The range’s rugged terrain and rivers support unique flora adapted to monsoon climates.studyiq+2



Cultural and Economic Importance
The Satpura region has been home to tribal communities such as the Gond, Bhil, and Korku, who have lived in harmony with nature for centuries. Economically, the range contributes through:
-
Forestry
-
Agriculture
-
Mineral resources
-
Eco-tourism
Location of the Satpura Range in India (Map Explanation)
The Satpura Range lies in central India, between the Narmada River to the north and the Tapti River to the south.